linux字符設(shè)備有:1、鼠標(biāo),是計(jì)算機(jī)的一種外接輸入設(shè)備,也是計(jì)算機(jī)顯示系統(tǒng)縱橫坐標(biāo)定位的指示器;2、鍵盤,是用于操作計(jì)算機(jī)設(shè)備運(yùn)行的一種指令和數(shù)據(jù)輸入裝置;3、串行端口終端,使用計(jì)算機(jī)串行端口連接的終端設(shè)備;4、控制終端;5、控制臺(tái)等。

本教程操作環(huán)境:linux7.3系統(tǒng)、Dell G3電腦。
linux字符設(shè)備
字符設(shè)備是Linux三大設(shè)備之一(另外兩種是塊設(shè)備,網(wǎng)絡(luò)設(shè)備)。它們均以一個(gè)文件節(jié)點(diǎn)形式顯示在文件系統(tǒng)的/dev目錄下(crw–w—- 1 root tty 4, 0 7月 11 09:11 tty0 其中c代表字符設(shè)備類型)。
字符設(shè)備是指設(shè)備無(wú)需緩沖即可直接進(jìn)行讀寫(xiě)的設(shè)備, 如鼠標(biāo),鍵盤,串口設(shè)備、調(diào)制解調(diào)器等, 它與塊設(shè)備的區(qū)別在于是字符操作的基本單位是字節(jié)。
字符設(shè)備的分類
字符設(shè)備主要包括控制終端設(shè)備和串行終端設(shè)備, 例如控制臺(tái)和鍵盤。依據(jù)功能和硬件上的差別, 字符終端設(shè)備有如下分類:
-
串行端口終端(/dev/ttSn):使用計(jì)算機(jī)串行端口連接的終端設(shè)備, 串行設(shè)備數(shù)據(jù)傳輸方式為同一字符8個(gè)bit單線傳輸, 在命令行輸入 echo 'hello world' > /dev/ttyS0可將輸入寫(xiě)入到對(duì)應(yīng)設(shè)備。
-
偽終端(/dev/ttyp,/dev/ptyp): 對(duì)應(yīng)底層不存在真實(shí)的硬件設(shè)備, 用于為其他程序提供終端式樣的接口,如網(wǎng)絡(luò)登陸主機(jī)時(shí)網(wǎng)絡(luò)服務(wù)器和shell程序之間的終端接口。
-
控制終端(/dev/tty):主設(shè)備號(hào)為5, 進(jìn)程控制終端,與進(jìn)程相關(guān)聯(lián),如登陸shell進(jìn)程使用的就是終端/dev/tty。
-
控制臺(tái)(/dev/ttyn,/dev/consol): 計(jì)算機(jī)輸入輸出的顯示器,當(dāng)控制臺(tái)登陸時(shí), 使用的就是tty1, 而ubuntu 圖形界面使用的tty7。
-
其他類型:現(xiàn)行的linux針對(duì)許多不同的設(shè)備建有許多其他種類的設(shè)備特殊文件,如ISIDIN設(shè)備的/dev/ttyIn設(shè)備。
字符設(shè)備的性質(zhì)及特點(diǎn)
-
字符設(shè)備屬于設(shè)備文件系統(tǒng)的一種, 相當(dāng)于底層硬件向上層提供的邏輯設(shè)備文件, 宛如將一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)端口(數(shù)據(jù)寄存器)與一個(gè)文件對(duì)接起來(lái),設(shè)備驅(qū)動(dòng)程序直接對(duì)文件操作, 于是便直接對(duì)端口進(jìn)行了讀寫(xiě)操作。 同樣作為文件, 字符設(shè)備驅(qū)動(dòng)也必須實(shí)現(xiàn)文件的基本的操作open(),close(),write(),read()等,當(dāng)然終端重定向操作也是支持的。
-
字符設(shè)備文件文件的讀寫(xiě)是以單個(gè)字節(jié)為單位的, 不需要設(shè)立硬件緩沖區(qū)。 設(shè)備像訪問(wèn)字節(jié)流一樣被操作系統(tǒng)訪問(wèn)。 字節(jié)流就像在硬件端口和文件系統(tǒng)搭建起了一個(gè)傳送管道, 字節(jié)逐個(gè)通過(guò)管道傳輸并呈現(xiàn)給讀寫(xiě)雙方。 這個(gè)流特性在驅(qū)動(dòng)程序中是以緩沖隊(duì)列來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的。例如: 控制臺(tái)的結(jié)構(gòu)體中的讀寫(xiě)緩沖隊(duì)列
struct tty_struct { struct termios termios; int pgrp; int stopped; void (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty); struct tty_queue read_q; //讀隊(duì)列 struct tty_queue write_q; //寫(xiě)隊(duì)列 struct tty_queue secondary; //tty輔助隊(duì)列(存放規(guī)格化后的字符) };
-
字符設(shè)備由字符設(shè)備號(hào)標(biāo)識(shí)。字符設(shè)備號(hào)由主設(shè)備號(hào)和次設(shè)備號(hào)構(gòu)成, 例如/dev/ttyS0的設(shè)備號(hào)為(4,64); 主設(shè)備號(hào)標(biāo)識(shí)設(shè)備對(duì)應(yīng)驅(qū)動(dòng)程序, 內(nèi)核通過(guò)主設(shè)備號(hào)將設(shè)備和驅(qū)動(dòng)程序一一對(duì)應(yīng)起來(lái), 次設(shè)備號(hào)由驅(qū)動(dòng)程序使用, 用于驅(qū)動(dòng)程序內(nèi)部區(qū)分設(shè)備細(xì)節(jié)差別使用的代碼,內(nèi)核其他部分不使用它。
字符設(shè)備在應(yīng)用層如何體現(xiàn)
cat /proc/devices 命令可以查看當(dāng)前系統(tǒng)中所有的字符設(shè)備和塊設(shè)備。
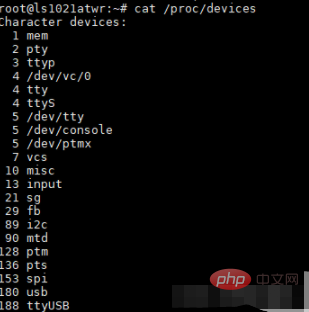
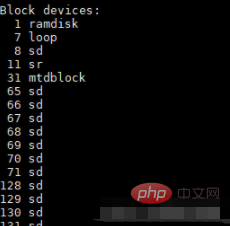
在Linux 中一切接文件,設(shè)備也被抽象成文件,在/dev/ 目錄下可以查看到字符設(shè)備和塊設(shè)備的對(duì)應(yīng)的文件。
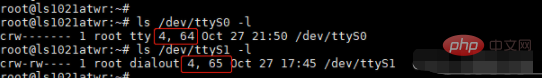
例如這是兩個(gè)串口設(shè)備文件,使用ls -l 查看它的詳細(xì)信息。
與普通文件不同的是設(shè)備文件沒(méi)有大小,而是被替換成了設(shè)備號(hào)(主設(shè)備號(hào)和次設(shè)備號(hào)),設(shè)備號(hào)可以與/proc/devices 中的信息相對(duì)應(yīng)。
如何訪問(wèn)一個(gè)設(shè)備?
既然它被抽象成了一個(gè)文件,那么自然就用文件IO (open、read、write 等等) 來(lái)訪問(wèn)。
設(shè)備號(hào)
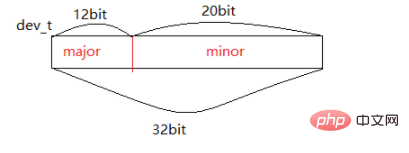
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major,minor)major = MAJOR(dev)minor = MINOR(dev)
設(shè)備號(hào)由major和minor 組成,總共32位,高12位為major,低20位為minor。每一個(gè)設(shè)備號(hào)都唯一對(duì)應(yīng)著一個(gè)cdev結(jié)構(gòu)體。
注冊(cè)字符設(shè)備首先要申請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)備號(hào),可以一次批量的申請(qǐng)多個(gè)設(shè)備號(hào)(相同的major,依次遞增的minor)。
如果沒(méi)有指定主設(shè)備號(hào)的話就使用如下函數(shù)來(lái)申請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)備號(hào):int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name)
baseminor:起始的minor值。
count:一共申請(qǐng)幾個(gè)設(shè)備號(hào)。申請(qǐng)到的設(shè)備號(hào)在(MKDEV(major,baseminor) ~ MKDEV(major,baseminor+count)) 范圍內(nèi)。
(自動(dòng)申請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)備號(hào)的原理,其實(shí)是傳遞一個(gè)major = 0,然后由內(nèi)核分配一個(gè)空閑的設(shè)備號(hào)返回)
如果給定了設(shè)備的主設(shè)備號(hào)和次設(shè)備號(hào)就使用如下所示函數(shù)來(lái)注冊(cè)設(shè)備號(hào)即可:int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
釋放設(shè)備號(hào):void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count)
字符設(shè)備結(jié)構(gòu)體 cdev
//include/linux/cdev.h struct cdev { struct kobject kobj; struct module *owner; const struct file_operations *ops; struct list_head list; dev_t dev; unsigned int count; };
常用
申請(qǐng)一個(gè)cdev 內(nèi)存:struct cdev *cdev_alloc(void);
初始化cdev->ops,即cdev->ops = &xxx_file_operation; :void cdev_init(struct cdev *, const struct file_operations *);
將填充好的cdev 實(shí)例,添加到cdev 鏈表。意味著向內(nèi)核注冊(cè)一個(gè)字符設(shè)備:int cdev_add(struct cdev *, dev_t, unsigned); //dev_t:添加cdev時(shí)必須要,傳遞一個(gè)dev_t,并且它與cdev是唯一對(duì)應(yīng)的。
cdev_add 添加過(guò)程中會(huì)綁定cdev 與dev_t。
從內(nèi)核刪除一個(gè)字符設(shè)備:void cdev_del(struct cdev *);
不常用
增加cdev 調(diào)用計(jì)數(shù):void cdev_put(struct cdev *p);
總結(jié):注冊(cè)字符設(shè)備的主要流程就是,申請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)備號(hào)dev_t,創(chuàng)建一個(gè)cdev、初始化cdev (cdev->ops)、向內(nèi)核添加 cdev(同時(shí)會(huì)綁定cdev 與dev_t)。
如果你嫌這些步驟太麻煩的話,內(nèi)核還提供了一個(gè)函數(shù)可以一步到位的注冊(cè)字符設(shè)備——__register_chrdev
它會(huì)申請(qǐng)多個(gè)設(shè)備號(hào),創(chuàng)建cdev并初始化它,然后用這多個(gè)設(shè)備號(hào)綁定同一個(gè)cdev 注冊(cè)。

還有一個(gè)register_chrdev,它是對(duì)__register_chrdev 的封裝,次設(shè)備號(hào)從基值0開(kāi)始,直接申請(qǐng)了256 個(gè)次設(shè)備號(hào)。static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name, const struct file_operations *fops) { return __register_chrdev(major, 0, 256, name, fops); }
struct file_operations
字符設(shè)備在/dev/ 目錄下創(chuàng)建設(shè)備文件,并通過(guò)struct file_operations 向應(yīng)用層提供控制接口。應(yīng)用層對(duì)應(yīng)的open、read 等函數(shù)會(huì)調(diào)用到file_operations 對(duì)應(yīng)的函數(shù)。
//include/linux/fs.h struct file_operations { struct module *owner; loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int); ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *); ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *); ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *); int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *); unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); int (*mremap)(struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id); int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync); int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync); int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int); unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long); int (*check_flags)(int); int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *); ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int); ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int); int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **); long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset, loff_t len); void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f); #ifndef CONFIG_MMU unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *); #endif };
copy_to_user() 與 copy_from_user()
為了安全考慮,應(yīng)用進(jìn)程不能直接訪問(wèn)內(nèi)核數(shù)據(jù),需要借助這兩個(gè)函數(shù)拷貝:static inline int copy_to_user(void __user volatile *to, const void *from, unsigned long n)static inline int copy_from_user(void *to, const void __user volatile *from, unsigned long n)
返回非0 表示錯(cuò)誤。
自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建設(shè)備文件
自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建設(shè)備節(jié)點(diǎn)的工作是在驅(qū)動(dòng)程序的入口函數(shù)中完成的,一般在 cdev_add 函數(shù)后面添加自動(dòng)創(chuàng)建設(shè)備節(jié)點(diǎn)相關(guān)代碼。首先要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建一個(gè) class 類, class 是個(gè)結(jié)構(gòu)體,定義在文件include/linux/device.h 里面。
使用 class_create 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)類:
extern struct class * __must_check __class_create(struct module *owner, const char *name, struct lock_class_key *key); #define class_create(owner, name) ({ static struct lock_class_key __key; __class_create(owner, name, &__key); })
使用class_destroy 摧毀一個(gè)類:extern void class_destroy(struct class *cls);
struct class { const char *name; struct module *owner; struct class_attribute *class_attrs; const struct attribute_group **dev_groups; struct kobject *dev_kobj; int (*dev_uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env); char *(*devnode)(struct device *dev, umode_t *mode); void (*class_release)(struct class *class); void (*dev_release)(struct device *dev); int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state); int (*resume)(struct device *dev); const struct kobj_ns_type_operations *ns_type; const void *(*namespace)(struct device *dev); const struct dev_pm_ops *pm; struct subsys_private *p; };
在創(chuàng)建完類后,要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建一個(gè)設(shè)備,使用 device_create創(chuàng)建一個(gè)設(shè)備:struct device *device_create(struct class *cls, struct device *parent, dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...);
摧毀一個(gè)設(shè)備:extern void device_destroy(struct class *cls, dev_t devt);
創(chuàng)建類會(huì)在/sys/class/ 目錄下生成一個(gè)新的文件夾,其中包含屬于此類的設(shè)備文件夾。
IS_ERR 和 PTR_ERR
IS_ERR 可以判斷一個(gè)指針是否為空,PTR_ERR 將指針轉(zhuǎn)化為數(shù)值返回。
static inline long __must_check PTR_ERR(const void *ptr) { return (long) ptr; } static inline long __must_check IS_ERR(const void *ptr) { return IS_ERR_VALUE((unsigned long)ptr); }
#include <linux/fs.h> //file_operations聲明 #include <linux/module.h> //module_init module_exit聲明 #include <linux/init.h> //__init __exit 宏定義聲明 #include <linux/device.h> //class devise聲明 #include <linux/uaccess.h> //copy_from_user 的頭文件 #include <linux/types.h> //設(shè)備號(hào) dev_t 類型聲明 #include <asm/io.h> //ioremap iounmap的頭文件 #define DEVICE_CNT 0 //設(shè)備號(hào)個(gè)數(shù) struct led_device{ dev_t devid; //設(shè)備號(hào) int major; //主設(shè)備號(hào) int minor; //次設(shè)備號(hào) char* name = "led"; //驅(qū)動(dòng)名 struct cdev led_dev; //cdev 結(jié)構(gòu)體 struct class *class; /* 類 */ struct device* device; //設(shè)備 }; struct led_device led; static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp) { return 0; } static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) { return 0; } static ssize_t led_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt) { return 0; } /* 設(shè)備操作函數(shù) */ static struct file_operations led_fo = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = led_open, .read = led_read, .write = led_write, }; static int _init led_init() { /*注冊(cè)字符設(shè)備驅(qū)動(dòng)*/ /*1.注冊(cè)設(shè)備號(hào)*/ led.major = 0; //由內(nèi)核自動(dòng)分配主設(shè)備號(hào) if(led.major) //如果分配了的話就注冊(cè) { led.devid = MKDEV(led.major,0); register_chrdev_region(led.devid,DEVICE_CNT,led.name); //將驅(qū)動(dòng)注冊(cè)到內(nèi)核中 } else{ //如果沒(méi)有分配的話 //從0號(hào)(次設(shè)備號(hào))開(kāi)始申請(qǐng) alloc_chrdev_region(&led.devid,0,DEVICE_CNT,led.name); //申請(qǐng)?jiān)O(shè)備號(hào) led.major = MAJOR(led.devid); //獲取主設(shè)備號(hào) led.minor = MANOR(led.devid); //獲取次設(shè)備號(hào) } printk("newcheled major=%d,minor=%drn",newchrled.major, newchrled.minor); /*2.初始化 cdev 結(jié)構(gòu)體*/ led.led_dev.woner = THIS_MODULE; cdev_init(&led.led_dev,&led_fo); //將操作函數(shù)初始化到cdev結(jié)構(gòu)體 /*3.應(yīng)該是向鏈表中添cdev*/ cdev_add(&led.led_dev,led.devid,DEVICE_CNT); /*4.創(chuàng)建節(jié)點(diǎn)*/ led.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE,led.name); //先創(chuàng)建一個(gè)類 led.device = device_create(led.class,NULL,led.devid,NULL); //創(chuàng)建設(shè)備 return 0; } static void _exit led_exit() { /* 注銷字符設(shè)備驅(qū)動(dòng) */ cdev_del(&newchrled.cdev);/* 刪除cdev */ unregister_chrdev_region(newchrled.devid, NEWCHRLED_CNT); /* 注銷設(shè)備號(hào) */ device_destroy(newchrled.class, newchrled.devid); class_destroy(newchrled.class); } /*注冊(cè)字符設(shè)備入口與卸載入口*/ module_init(led_init); module_exit(led_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2"); MODULE_AUTHOR("zhoujianghong");
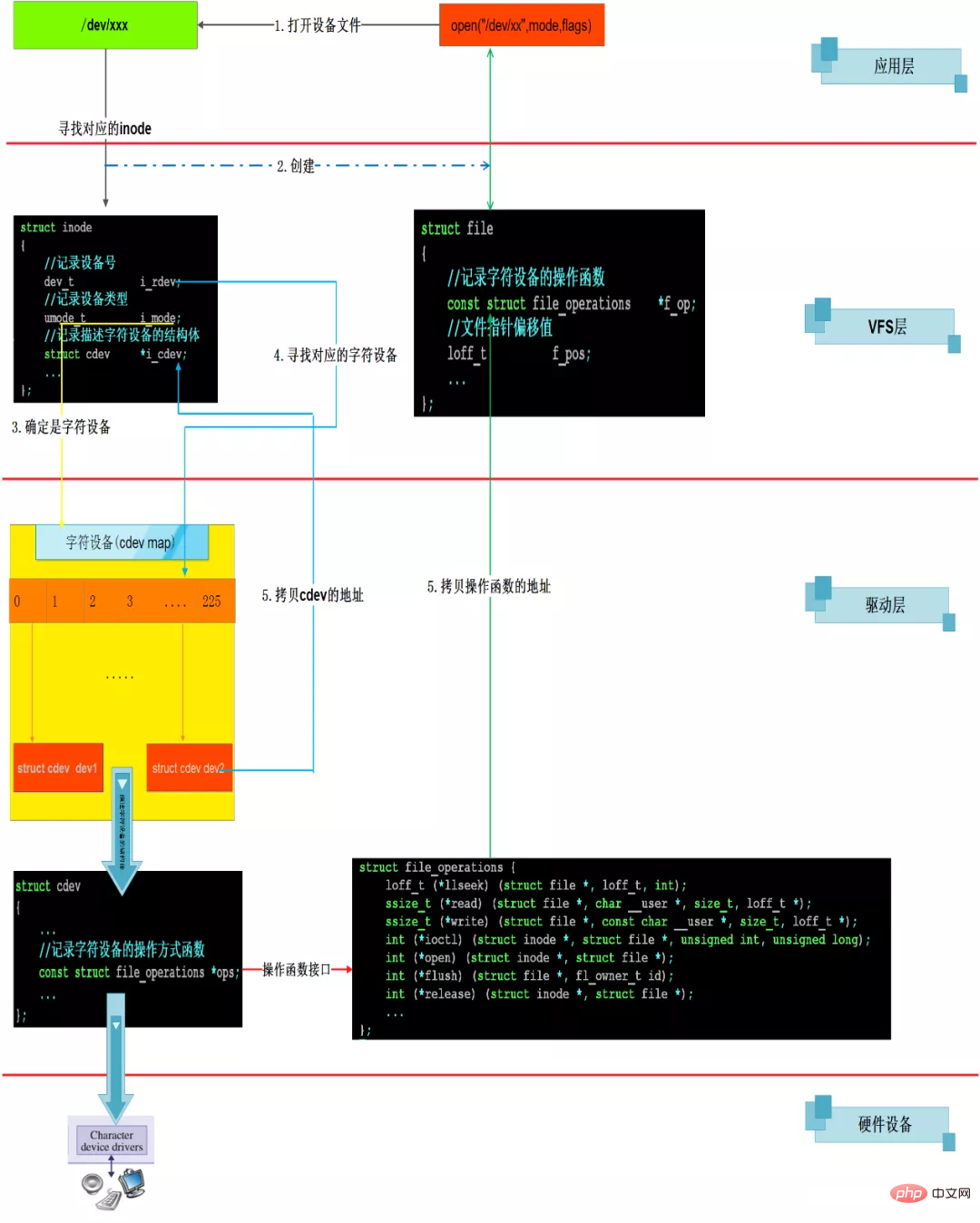
應(yīng)用open到file_operations->open 的調(diào)用原理
 站長(zhǎng)資訊網(wǎng)
站長(zhǎng)資訊網(wǎng)